Description
Spartan Chess is a chess variant where two different entirely armies combat each other.
The Persian army (white) is the normal FIDE army (which, as we know, was brought to us via Persia). The Spartans (black) are ruled by two Kings, of which at least one must be ounattacked after your turn. But the other can be sacrificed (and then re-obtained by promotion). All other Spartan pieces, including the Hoplit 'Pawns', are unorthodox pieces.

Rules
Differences from orthodox chess
The black army ('Spartans') consists, apart from the two Kings, entirely of fairy pieces, of 5 different types:
- The Warlord (aka Archbishop or Cardinal): moves and captures like Knight + Bishop

- The General (aka Crowned Rook or Dragon King): moves and captures like Rook or King

- The Lieutenant: moves and captures 1 or 2 steps (jumping) diagonally,
or can step to an adjacent empty square left or right.

- The Captain (aka Woody Rook): moves and captures 1 or 2 steps (jumping) orthogonally.

- The Hoplit: moves 1 step diagonally forward, and captures one step straight ahead.
In its initial location it can also jump 2 steps diagonally forward to an empty square.

Inital setup

The white player starts with the Persian army, consisting of:
- 8 Pawns
- 2 Knights
- 2 Bishops
- 2 Rooks
- 1 Queen
- 1 King
The black player starts with the Spartan army, consisting of:
- 8 Hoplits
- 2 Captains
- 2 Lieutenants
- 1 General
- 1 Warlord
- 2 Kings
Castling: only the Persians can castle.
Double move for Pawns and Hoplits (start): yes, and the Hoplits jump.
"En passant" capture: no. The Hoplits do not really pass through Pawn attack with their jumping move, and for Hoplits it is geometrically impossible to have an attack on the square Pawns pass through.
Checking: The rules for checking are generalized to the Spartan King pair as follows: you are in check if you have not at least one unattacked King. As usual, when you have no moves that resolve that condition, you are checkmated. Because one King can be left attacked, it can also be captured.
Stalemate: when not in (generalized) check, but without legal moves, the game ends as a draw.
Promotion: Pawns promote as in orthodox Chess. Hoplits promote upon reaching the 1st rank to Spartan pieces only. They can also promote the King, if that will not make the number of Spartan Kings exceed two.
Please see below for orthodox Chess rules.
Orthodox Chess rules
The following text is extracted from Wikipedia, under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 3.0 License. For more details and references, please access the original article.
Chess is a game played by two people on a chessboard, with sixteen pieces (of six types) for each player. Each type of piece moves in a distinct way. The goal of the game is to checkmate, i.e. to threaten the opponent's king with inevitable capture. In addition, there are several ways that a game can end in a draw.
Initial setup
Chess is played on a chessboard, a square board divided into 64 squares (eight-by-eight) of alternating color, which is similar to that used in draughts (checkers). No matter what the actual colors of the board, the lighter-colored squares are called "light" or "white", and the darker-colored squares are called "dark" or "black". Sixteen "white" and sixteen "black" pieces are placed on the board at the beginning of the game. The board is placed so that a white square is in each player's near-right corner.
Each player controls sixteen pieces:
| Name | Number | White Symbols | Black Symbols |
| King | 1 |  |
 |
| Queen | 1 |  |
 |
| Rook | 2 |  |
 |
| Bishop | 2 |  |
 |
| Knight | 2 |  |
 |
| Pawn | 8 |  |
 |
At the beginning of the game, the pieces are arranged as shown in the diagram. The second row from the player contains the eight pawns; the row nearest the player contains the remaining pieces. Popular phrases used to remember the setup, often heard in beginners' clubs, are "queen on her own color" and "white on right". The latter refers to setting up the board so that the square closest to each player's right is white.
Play of the game
The player controlling the white army is named "White"; the player controlling the black pieces is named "Black". White moves first, then players alternate moves. Making a move is required; it is not legal to skip a move, even when having to move is detrimental. Play continues until a king is checkmated, a player resigns, or a draw is declared, as explained below. In addition, if the game is being played under a time control players who exceed their time limit lose the game.
Movement
Basic moves
Each chess piece has its own method of movement. Moves are made to vacant squares except when capturing an opponent's piece.
With the exception of any movement of the knight and the occasional castling maneuver, pieces cannot jump over each other. When a piece is captured (or taken), the attacking piece replaces the enemy piece on its square (en passant being the only exception). The captured piece is thus removed from the game and may not be returned to play for the remainder of the game. The king can be put in check but cannot be captured (see below).
King

The king can move exactly one square horizontally, vertically, or diagonally. Only once per player, per game, is a king allowed to make a special move known as castling (see below).
Rooks
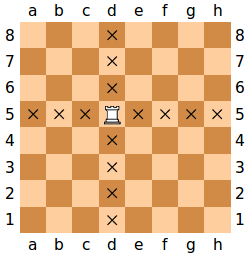
The rook moves any number of vacant squares vertically or horizontally. It also is moved while castling.
Bishops
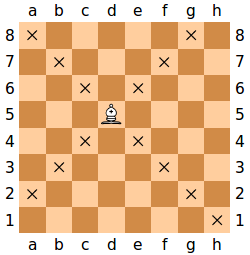
The bishop moves any number of vacant squares in any diagonal direction.
Queen

The queen can move any number of vacant squares diagonally, horizontally, or vertically.
Knights

The knight moves to the nearest square not on the same rank, file, or diagonal. In other words, the knight moves two squares horizontally then one square vertically, or one square horizontally then two squares vertically. Its move is not blocked by other pieces: it jumps to the new location.
Pawns

Pawns have the most complex rules of movement:
- A pawn can move forward one square, if that square is unoccupied. If it has not yet moved, each pawn has the option of moving two squares forward provided both squares in front of the pawn are unoccupied. A pawn cannot move backwards.
- Pawns are the only pieces that capture differently from how they move. They can capture an enemy piece on either of the two spaces adjacent to the space in front of them (i.e., the two squares diagonally in front of them) but cannot move to these spaces if they are vacant.
The pawn is also involved in the two special moves en passant and promotion.
Castling
Castling consists of moving the king two squares towards a rook, then placing the rook on the other side of the king, adjacent to it. Castling is only permissible if all of the following conditions hold:
- The king and rook involved in castling must not have previously moved;
- There must be no pieces between the king and the rook;
- The king may not currently be in check, nor may the king pass through or end up in a square that is under attack by an enemy piece (though the rook is permitted to be under attack and to pass over an attacked square);
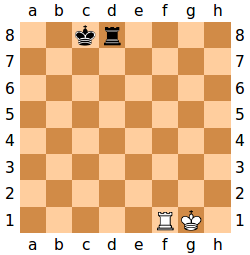

En passant

If player A's pawn moves forward two squares and player B has a pawn on its fifth rank on an adjacent file, B's pawn can capture A's pawn as if A's pawn had only moved one square. This capture can only be made on the immediately subsequent move. In this example, if the white pawn moves from a2 to a4, the black pawn on b4 can capture it en passant, ending up on a3.
Pawn promotion
If a pawn advances to its eighth rank, it is then promoted (converted) to a queen, rook, bishop, or knight of the same color, the choice being at the discretion of its player (a queen is usually chosen). The choice is not limited to previously captured pieces. Hence it is theoretically possible for a player to have up to nine queens or up to ten rooks, bishops, or knights if all of their pawns are promoted. If the desired piece is not available, the player should call the arbiter to provide the piece.
Check

A king is in check when it is under attack by one or more enemy pieces. A piece unable to move because it would place its own king in check (it is pinned against its own king) may still deliver check to the opposing player.
A player may not make any move which places or leaves his king in check. The possible ways to get out of check are:
- Move the king to a square where it is not threatened.
- Capture the threatening piece (possibly with the king).
- Block the check by placing a piece between the king and the opponent's threatening piece.
End of the game
Checkmate
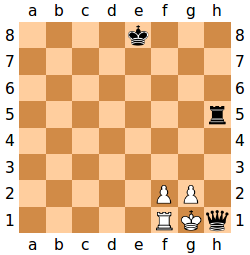
If a player's king is placed in check and there is no legal move that player can make to escape check, then the king is said to be checkmated, the game ends, and that player loses. Unlike other pieces, the king is never actually captured or removed from the board because checkmate ends the game.
The diagram shows a typical checkmate position. The white king is threatened by the black queen; every square to which the king could move is also threatened; it cannot capture the queen, because it would then be threatened by the rook.
Draws

The game ends in a draw if any of these conditions occur:
- The game is automatically a draw if the player to move is not in check but has no legal move. This situation is called a stalemate. An example of such a position is shown in the diagram to the right.
The game is immediately drawn when there is no possibility of checkmate for either side with any series of legal moves. This draw is often due to insufficient material, including the endgames
- king against king;
- king against king and bishop;
- king against king and knight;
- king and bishop against king and bishop, with both bishops on diagonals of the same color.
- Both players agree to a draw after one of the players makes such an offer.
The player having the move may claim a draw by declaring that one of the following conditions exists, or by declaring an intention to make a move which will bring about one of these conditions:
- Fifty-move rule: There has been no capture or pawn move in the last fifty moves by each player.
- Threefold repetition: The same board position has occurred three times with the same player to move and all pieces having the same rights to move, including the right to castle or capture en passant.
If the claim is proven true, the game is drawn.
At one time, if a player was able to check the opposing king continually (perpetual check) and the player indicated their intention to do so, the game was drawn. This rule is no longer in effect; however, players will usually agree to a draw in such a situation, since either the rule on threefold repetition or the fifty-move rule will eventually be applicable.
Credits
Rules
Steven Streetman, 2010
Jocly implementation
- Development: Michel gutierrez (@_mig_) and H.G.Muller (TalkChess forum)
- Graphic design: Michel gutierrez (@_mig_) and Jérôme Choain (@jcfrog)